Your monitor flickers with the promise of high-fidelity graphics – stunning vistas, intricate character models, and buttery-smooth animation. But then, reality hits: choppy framerates, the kind that yank you out of the immersive spell a game tries to weave. What if you could double your frames without upgrading your expensive GPU? That's the core promise of Understanding Frame Generation Technology: What It Is and How It Works, a game-changer that's reshaping how we think about performance and visual quality.
This isn't just about rendering more pixels; it's about intelligent computing, where AI steps in to create frames that your graphics card never had to touch. It’s a leap beyond traditional rendering, a shift towards smarter, more efficient gaming experiences.
At a Glance: Frame Generation Explained
- AI-Powered Performance: Frame generation uses artificial intelligence to create entirely new frames, slotting them in between those rendered by your GPU.
- Massive FPS Boosts: Expect significantly higher frame rates, often doubling or more, especially in demanding games at high resolutions.
- Smoother Visuals: By increasing frame density, the technology delivers a more fluid and consistent visual experience, reducing stutter and improving overall motion clarity.
- Not Upscaling: It's distinct from upscaling technologies (like DLSS Super Resolution) which enhance existing frames; frame generation invents new ones. They can, however, work together.
- Potential Drawbacks: Can introduce visual artifacts (ghosting) and increase input latency, making it generally unsuitable for competitive online multiplayer.
- The Future of Gaming: An evolving technology with the potential to transform performance across PCs and consoles, making high-fidelity gaming more accessible.
The AI Revolution for Your Graphics Card: What Exactly Is Frame Generation?
Imagine your favorite movie, but instead of just showing you the frames the director filmed, a sophisticated AI analyzes the movement between two existing frames and creates a brand-new, highly plausible frame right in the middle. That’s essentially what frame generation does for your games.
Instead of your graphics processing unit (GPU) meticulously rendering every single frame – a computationally intensive task – it focuses on rendering key frames, say "Frame One" and "Frame Three." Then, a specialized AI model steps in, meticulously analyzing the motion and visual data from these two GPU-rendered frames. Its mission? To predict and generate "Frame Two," a seamlessly integrated intermediate frame that never existed before. This process can extend to "Multi Frame Generation," where several frames might be generated for every one the GPU renders, sometimes making three out of every four frames you see a product of AI, not raw GPU power.
This innovative approach allows your GPU to breathe. It reduces its workload dramatically, freeing it up to handle other intensive tasks like complex ray tracing calculations, all while delivering a higher perceived frame rate to your screen. It's not magic, but it certainly feels like it, offering a significant performance uplift that was previously only achievable through expensive hardware upgrades.
Frame Generation vs. Upscaling: Not the Same Beast (But They Play Nice)
It's easy to confuse frame generation with other performance-enhancing technologies like upscaling, often known by names like NVIDIA's DLSS Super Resolution or AMD's FSR (FidelityFX Super Resolution) 1.0/2.0. But while both aim to boost your game's visual performance, they tackle the problem from fundamentally different angles.
Upscaling works like a smart magnifying glass. Your GPU renders a game at a lower resolution – say, 1080p – to save on processing power. Then, a sophisticated algorithm (often AI-enhanced) takes that lower-resolution image and intelligently "upscales" or reconstructs it to a higher target resolution, such as 4K. It's enhancing the pixels that are already there, filling in the blanks to make a sharper, higher-resolution image from a smaller source.
Frame generation, on the other hand, isn't about existing pixels or resolutions. It's about creating new frames entirely. It doesn't enhance a 1080p frame to 4K; it takes a 1080p frame and another 1080p frame (or 4K and 4K) and inserts a brand-new 1080p (or 4K) frame between them. Think of it as interpolating motion to create additional animation cells, making the overall movement smoother.
The truly exciting part? These two technologies aren't mutually exclusive. In fact, they're often used in tandem for maximum impact. You can run your game at a lower internal resolution with upscaling enabled, getting a sharp image at your target resolution, and then apply frame generation on top to dramatically increase the frame rate. This one-two punch delivers incredible performance gains, letting you push settings to ultra, even with ray tracing enabled, without your GPU breaking a sweat.
Under the Hood: How AI Crafts Those Extra Frames
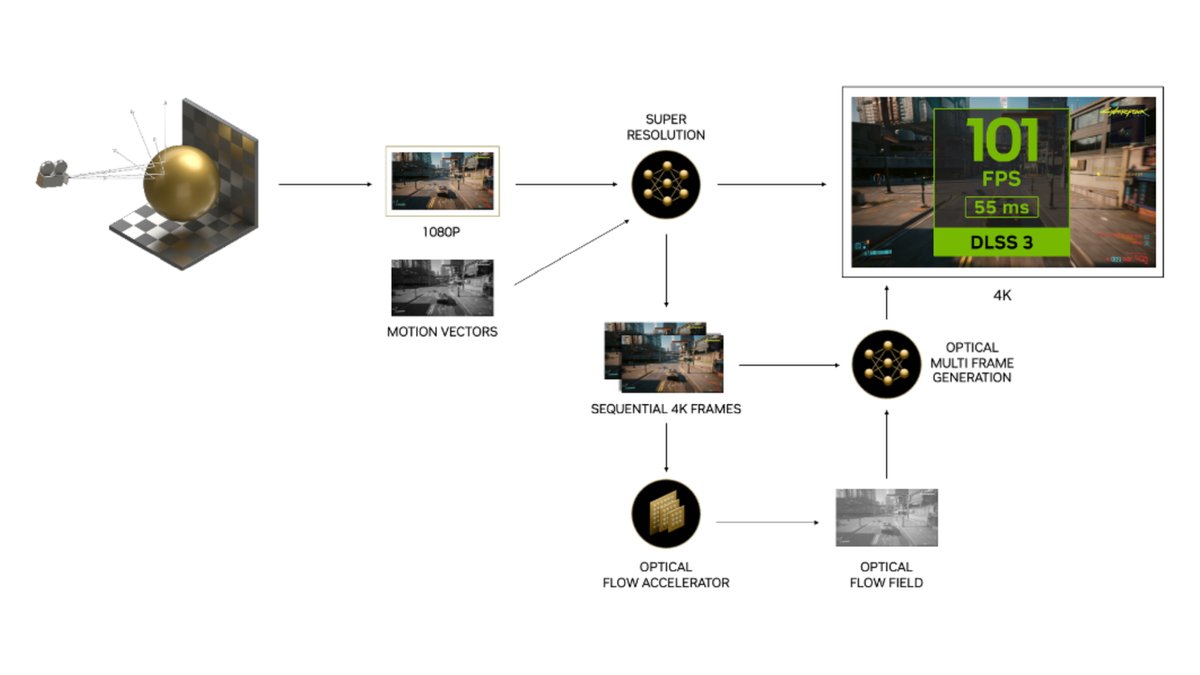
So, how does this AI wizardry actually work? It's all about predicting movement and visual information with incredible precision. Frame generation technologies, such as NVIDIA's DLSS Frame Generation and AMD's FSR 3, rely heavily on a critical piece of data: motion vectors.
Motion vectors are essentially directional arrows embedded within each rendered frame, telling the GPU exactly how objects, characters, and even individual pixels are moving from one frame to the next. Think of them as a detailed blueprint of all the action happening on screen.
When the GPU renders "Frame One" and "Frame Three," it also generates these motion vectors. This rich motion data is then fed into a deep learning AI model. The AI processes these vectors, identifying patterns, trajectories, and deformations. It understands, for instance, that a character's arm is swinging from point A to point B, or that a car is moving across the screen at a certain speed. Based on this understanding, the AI predicts what the intermediate "Frame Two" should look like – down to the smallest detail.
NVIDIA's approach, particularly with its RTX 40-series GPUs, takes this a step further. These cards feature dedicated hardware components called Optical Flow Accelerators. These accelerators are specifically designed to track incredibly fine details – think subtle shadow shifts, complex reflections on water, or the individual particles in an explosion – and generate even more precise motion data. This highly granular information is then fed to the AI model, allowing it to generate intermediate frames that are remarkably accurate and visually convincing, making transitions feel incredibly seamless. It's this continuous feedback loop of precise motion data and an intelligent AI model that allows frame generation to create new visual information that often fools the eye into believing it was fully rendered by the GPU.
The Game-Changing Benefits: Why You'll Love Frame Generation
For many gamers, frame generation isn't just a nice-to-have feature; it's a transformative technology that unlocks gaming experiences previously out of reach. Here’s why it’s generating so much excitement:
A Performance Boost That Feels Unreal
This is the headline feature: frame generation delivers truly staggering performance improvements. Imagine turning a stuttering 45 frames per second (FPS) in a graphically intense title, running at a demanding 4K resolution with all the bells and whistles, into a silky-smooth 90+ FPS. That's not an exaggeration; it's a common outcome. This substantial increase in frame rates means you can crank up settings like ray tracing, which are notorious performance hogs, without fear of your game grinding to a halt. It achieves this by shifting the burden of frame creation from the GPU's raw rendering power to the efficiency of an AI model, essentially giving you "free" performance headroom.
Smoother Visuals, Less Eye Strain
Higher frame rates don't just feel faster; they make everything on screen look and feel smoother. Motion blur, stuttering, and judder are significantly reduced. This improved frame pacing – the consistent delivery of frames to your monitor – results in a far more fluid and stable gaming experience. Your eyes don't have to work as hard to track movement, leading to less eye strain and a more comfortable, immersive session, even during long playtimes. Fast-paced action becomes clearer, and panning across detailed environments feels natural and effortless.
Meeting the Demands of Modern Gaming
Today's AAA titles are visual masterpieces, pushing boundaries with photorealistic graphics, expansive worlds, and cutting-edge effects like ray tracing. Running these games at high resolutions (like 4K) and targeting high refresh rates (60-240fps) demands immense GPU power. Frame generation acts as a crucial bridge, allowing current-generation hardware to meet these escalating demands without compromising visual fidelity. It's a key enabler for experiencing games as developers intended, often at frame rates that would otherwise require the most expensive, top-tier graphics cards.
The "Free Performance Boost" for Greater Value
When paired with upscaling technologies, frame generation offers an incredible value proposition. It allows gamers to achieve high-quality, high-performance experiences without constantly needing to buy the absolute latest and most expensive hardware. It extends the lifespan of your existing GPU, making high-fidelity gaming more accessible and affordable. It's like getting an instant hardware upgrade through software, empowering more players to enjoy premium visuals and smooth gameplay without breaking the bank.
The Catch: When Frame Generation Shows Its Flaws
While frame generation is a powerful tool, it's not a magic bullet without its caveats. Like any advanced technology, it has situations where its performance might not be ideal. Understanding these limitations is key to deciding when and where to enable it. This is where the debate about frame generation: good or bad? often begins.
Visual Artifacts: The Ghost in the Machine
The effectiveness of frame generation isn't uniform across all games or all systems. Because the AI is predicting what an inserted frame should look like, there's always a slight chance of misprediction. This can manifest as visual artifacts, the most common being ghosting or smearing. This is when a trailing "ghost" image appears behind moving objects, or details seem to smear across the screen.
These artifacts are often more noticeable in certain types of games and visual scenarios. In slower-paced, atmospheric games where graphical detail, subtle movements, and static elements are crucial – think the meticulously crafted environments of Alan Wake II – artifacts can be distracting and pull you out of the immersion. You might spot a strange shimmer around a character's hand or a slight distortion in a reflection.
Conversely, in fast-paced, chaotic games like Spider-Man 2, where action is constant and the screen is a blur of motion and effects, these subtle artifacts are far less apparent. The sheer speed and visual noise often mask any imperfections in the generated frames. Your brain is too busy processing explosions and web-slinging to notice a slight ghosting effect.
Latency in Competitive Games: A Millisecond Can Mean the Game
Perhaps the most significant downside, especially for a dedicated segment of the gaming community, is the impact on latency. Frame generation inherently complicates latency because it creates frames out of order. To generate "Frame Two" (the intermediate frame), the system needs data from "Frame Three" (the next fully rendered frame). This means "Frame Two" cannot be displayed until "Frame Three" is at least partially calculated, introducing a slight delay.
While human reaction time typically measures in hundreds of milliseconds, and a delay of 8.33 milliseconds (which is the time between frames at a buttery 120fps) might seem imperceptible to most, this added latency can be critical in highly competitive online games. In titles like Overwatch 2 or Fortnite, where every millisecond counts, an extra delay can literally be the difference between a headshot and a miss.
When you combine this frame generation latency with other sources of delay – your keyboard's input lag, your monitor's response time, server latency, and internet lag – the cumulative effect can be significant. Imagine a scenario in Overwatch 2, which uses a 64-tick server rate (meaning the server updates its state every 15.63ms). If your generated frame shows you hitting a target, but the server, due to accumulated latency, registers your input slightly later, you might experience a frustrating "desync" where your shot appears to hit on your screen but registers as a miss on the server.
For this reason, frame generation is generally considered a disadvantage for competitive online play. The minor visual imperfections are acceptable for single-player immersion, but the increased latency is a tangible handicap in a high-stakes, real-time multiplayer environment.
Who Should Use Frame Generation (And Who Should Think Twice)
Given its benefits and drawbacks, deciding whether to enable frame generation boils down to your personal gaming priorities and the specific games you play.
You should definitely consider using frame generation if:
- You prioritize visual fidelity and immersion in single-player games: If you love cranking up graphics settings, enabling ray tracing, and enjoying breathtaking visuals in titles like Cyberpunk 2077, Alan Wake II (despite potential minor artifacts), or Starfield, frame generation can provide a massive FPS boost to make those experiences incredibly smooth.
- You're playing at high resolutions (1440p, 4K) or with high refresh rate monitors: Frame generation excels at pushing performance in scenarios where your GPU is most strained, making high-resolution, high refresh rate gaming achievable on a wider range of hardware.
- You want to extend the life of your current GPU: It offers a significant performance uplift without requiring you to buy a new, expensive graphics card.
- You're already using upscaling technology: Frame generation works beautifully in conjunction with DLSS Super Resolution or FSR, offering a compounded performance increase.
You might want to think twice or avoid frame generation if: - You're a competitive online multiplayer gamer: For games like Valorant, CS:GO, Overwatch 2, or Call of Duty: Warzone, the added input latency can be a real detriment. In these titles, raw input responsiveness and the lowest possible latency are paramount.
- You are extremely sensitive to visual artifacts: If even minor ghosting or smearing breaks your immersion or bothers you, you might prefer to stick with native rendering, even at lower frame rates.
- Your GPU is already hitting very high frame rates (e.g., 200+ FPS): At extremely high frame rates, the relative benefit of frame generation might be less noticeable, while the absolute latency increase still exists. The law of diminishing returns applies here.
Ultimately, frame generation is an option, not a mandate. The best approach is to try it out in your favorite single-player games and see if you enjoy the performance boost without being bothered by any potential artifacts. For competitive games, it's generally best to keep it off.
The Road Ahead: Frame Generation's Transformative Future
Frame generation is still a relatively young technology, currently tied to specific, newer hardware like NVIDIA's RTX 40-series GPUs for DLSS Frame Generation and requiring compatible GPUs for AMD's FSR 3. However, its potential is immense, and its evolution is set to transform not just PC gaming, but potentially gaming across all platforms.
As the technology matures, we can expect several key developments:
- Broader Hardware Compatibility: While NVIDIA's DLSS Frame Generation currently relies on dedicated hardware (Optical Flow Accelerators), AMD's FSR 3 is designed to be more vendor-agnostic, working on a wider range of GPUs. This push for broader compatibility will democratize access to frame generation, making it available to more gamers across different hardware ecosystems.
- Refined AI Models: The deep learning AI models underpinning frame generation are constantly being improved. Future iterations will likely be even better at predicting frames, drastically reducing or even eliminating visual artifacts like ghosting and smearing. Expect generated frames to become virtually indistinguishable from natively rendered ones.
- Integration into Game Consoles: Consoles already utilize sophisticated rendering techniques like reconstruction and dynamic resolution scaling to maintain performance targets. Adding frame generation to their repertoire could provide a monumental performance boost without requiring major hardware redesigns. Imagine future console games consistently hitting 60fps or even 120fps with ray tracing enabled, simply by leveraging intelligent frame generation. This could make smoother console gaming with consistent frame pacing a standard expectation.
- A Shift Towards Smart Rendering: Frame generation marks a significant shift in the philosophy of game rendering. Instead of solely relying on brute-force raw hardware power, the industry is increasingly leveraging AI and intelligent rendering techniques to achieve performance targets. This approach is more sustainable, more efficient, and ultimately more adaptable to future visual demands, ensuring that stunning graphics remain accessible and playable for years to come.
This technology isn't just about making games faster; it's about making them smarter. It’s a testament to the power of AI in transforming interactive experiences, promising a future where visual fidelity and smooth performance are no longer a trade-off but a simultaneous reality.
Your Next Steps for Smoother Gaming
If you’re excited by the promise of frame generation, here’s how you can explore it and make the most of this cutting-edge technology:
- Check Your Hardware: Verify if your graphics card supports frame generation. NVIDIA's DLSS Frame Generation is currently exclusive to RTX 40-series GPUs. AMD's FSR 3 is more broadly compatible, though newer RDNA 3 GPUs (like RX 7000 series) will offer the best experience.
- Update Your Drivers: Always ensure you have the latest graphics drivers installed. These updates often include performance optimizations and support for new frame generation features.
- Look for Game Support: Frame generation needs to be integrated by game developers. Check if your favorite titles explicitly support DLSS Frame Generation or FSR 3. Most new AAA releases are quickly adopting these technologies.
- Experiment with Settings: Don't be afraid to dive into your game's graphics settings. Start by enabling frame generation, potentially alongside an upscaling option (like DLSS Quality or FSR Quality). Play for a bit, paying attention to both the framerate counter and any visual anomalies.
- Monitor Your Experience: Use an in-game FPS counter and an overlay that shows your latency (some graphics drivers offer this). If you find the visual boost and smoothness outweigh any minor artifacts or latency increases in single-player games, keep it on!
- Know When to Turn It Off: Remember the competitive gaming caveat. If you're heading into an online multiplayer match, it's generally best to disable frame generation to minimize input latency.
Frame generation is a powerful tool in the modern gamer's arsenal. By understanding how it works, its incredible benefits, and its specific limitations, you're now equipped to make informed decisions that will elevate your gaming experience, ushering in an era where AI-boosted performance is a standard, not a luxury.